Wrapping up and where to go
Overview
Teaching: 15 min
Exercises: 15 minQuestions
Where do I go now?
Objectives
Understand the basics in Nextflow pipelines and the options available.
Understand the next steps required.
The pipeline
Using the -with-dag option we can see the final flowchart
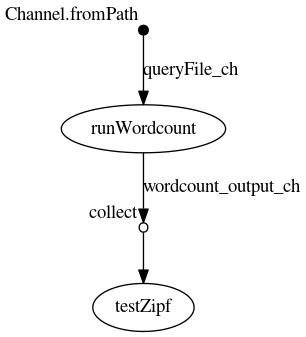
This doesnt show the particular runtime options but the raw dependency of the given processes in the Nextflow script.
This section shall document some of the questions raised in sessions.
Issues raised
- Chunking up data from channels.
When a list of files is send into a channel, a process can be defined to read an entry and process that one file. A case was raised where we may want to send 300 files to the channel and for a process to read 10 files from the channel at a time and perform a average on the data in the files. This can be achieved with the:
Channel
.from( 1,2,3,4,5,6 )
.take( 3 )
.subscribe onNext: { println it }, onComplete: { println 'Done' }
This example is taken from the documentation for Nextflow. This will produce:
1
2
3
Done
We could easily use this within our pipeline to process 2 files in the same process for example:
input:
tuple path(queryFile1), path(queryFile2) from queryFile_ch.collate(2)
output:
tuple path("${queryFile1.baseName}.dat"), path("${queryFile2.baseName}.dat") into wordcount_output_ch
script:
"""
python3 $PWD/../wordcount.py $queryFile1 ${queryFile1.baseName}.dat
python3 $PWD/../wordcount.py $queryFile2 ${queryFile2.baseName}.dat
"""
This will emit a tuple (people familiar with Python should know this term, think of it as a fixed list). Note the use
of collate on the input to the process. The output uses tuple to send both files to the output. A change is
required in the receiving process testZipf
input:
val x from wordcount_output_ch.flatten().collect()
The output from the run will look like:
$ nextflow run main.nf --query $PWD/../books/\*.txt
N E X T F L O W ~ version 20.10.0
Launching `main.nf` [magical_bardeen] - revision: dae9352cb9
I will count words of /nfshome/store01/users/c.sistg1/nf_training_Feb21/nextflow-lesson/work/../books/*.txt using wordcount.py and output o isles.dat
executor > local (3)
[54/2d1cdb] process > runWordcount (1) [100%] 2 of 2 ✔
[8b/217add] process > testZipf [100%] 1 of 1 ✔
This will first flatten the tuples into a list and then collect will emit all entries as a list to the val x.
Hopefully this shows the power of Nextflow is dealing with specific use cases.
- Self-learning
Due to time constraints during the sessions, opportunities to explore Nextflow at your own pace is limited. It would be good to setup a Nextflow community within the University to promote the use and encourage working together in solving common issues.
Interfaces to Nextflow
There are currently two interfaces to Nextflow that are being looked at:
- Nextflow Tower
Nextflow Tower is promoted by the developers of Nextflow. The cloud version is potentially a risk to store access keys to local resource such as the University supercomputer. There is a community edition on Github that suggests single users can run. Further investigation is required.
- DolphinNext
DolphinNext is an open project to provide an interface to Nextflow similar to Nextflow Tower. ARCCA currently has a test system up which we will go through during the live sessions. If users are interested in this please get in contact with us.
A tutorial to use DolphinNext is available on Github
Links to other resources
Key Points
Ask for help and support if you require assistance in writing pipelines on the supercomputer. The more we know people using it the better.